Conditional Functions
Overview
Time: 15 minObjectives
Introduction to Conditional Functions
FIXME
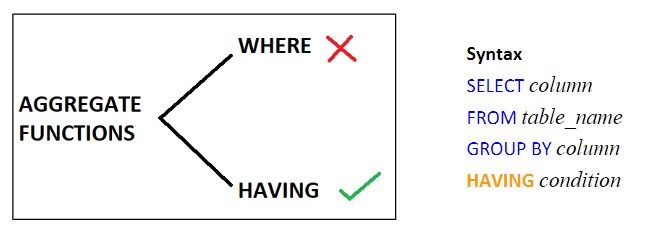
HAVING
The HAVING function performs a similar function as WHERE function and helps to filter out data in the result. The AGGREGATE functions cannot be used in WHERE clause and can only be used in the HAVING clause. Thus HAVING clause is generally preceded by the GROUP BY function.
Syntax
SELECT column
FROM table_name
GROUP BY column
HAVING condition
Example
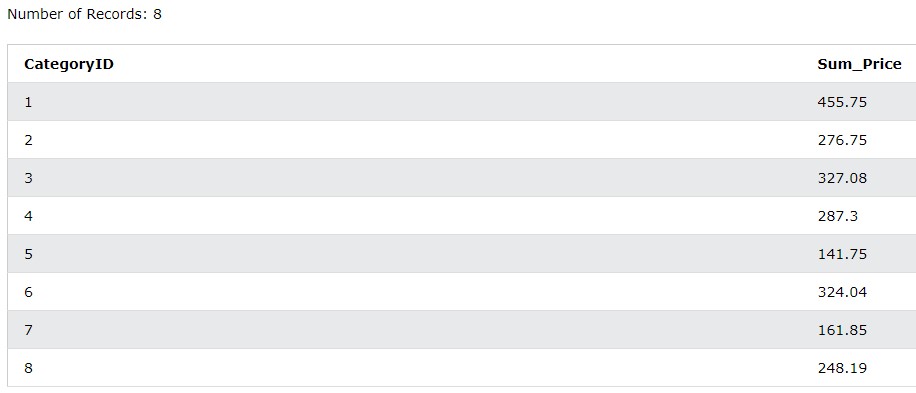
SELECT CategoryID, SUM(Price) AS Sum_Price
FROM Products
GROUP BY 1
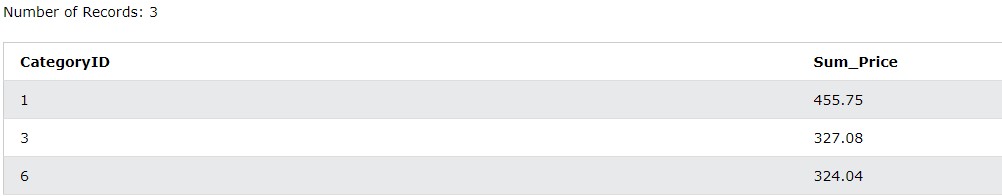
SELECT CategoryID, SUM(Price) AS Sum_Price
FROM Products
GROUP BY 1
HAVING SUM(Price) > 300
CASE
The CASE function/clause is used to perform an action based on a condition(s).It is similar to SWITCH CASE statement in programming languages
Syntax
SELECT column1, column2,
CASE WHEN condition1 THEN action1
WHEN condition2 THEN action2
ELSE action3 END
FROM table_name
Example
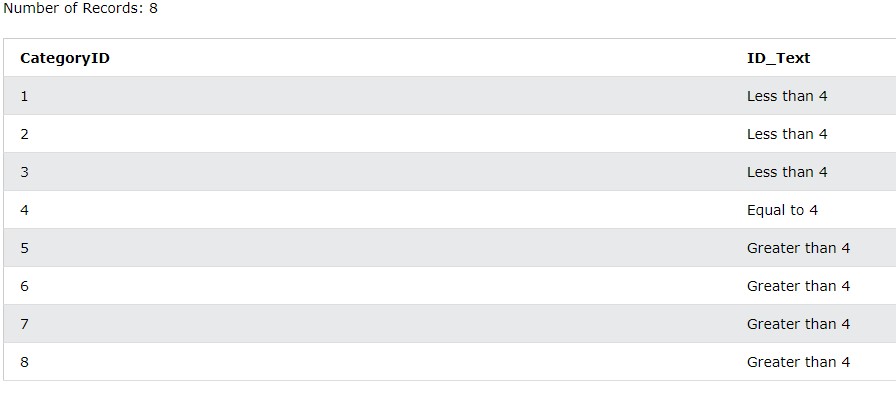
SELECT CategoryID,
CASE WHEN CategoryID < 4 THEN "Less than 4"
WHEN CategoryID = 4 THEN "Equal to 4"
ELSE "Greater than 4" END AS ID_Text
FROM Categories
IF (MySQL)
The IF functions is similar to the CASE function but performs only one of two actions based on a condition. If the condition is true then one action is performed else it automatically performs the other action.
Note: The IF function is available in MySQL and not the standard SQL language
Syntax
SELECT IF(condition, action_if_condition_true, action_if_condition_false)
FROM table_name
Example
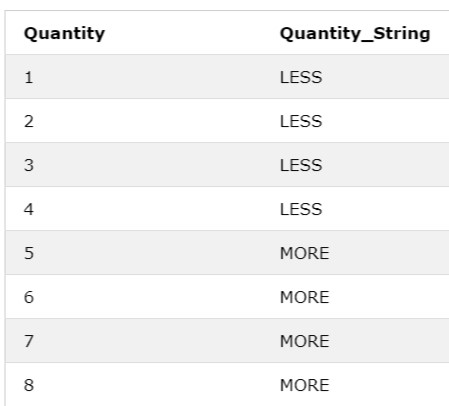
SELECT DISTINCT Quantity, IF(Quantity>4, "MORE", "LESS") AS Quantity_String
FROM OrderDetails
Key Points
Familiarize with the Conditional functions like HAVING, CASE, IF along with examples