Introduction to data frame
Overview
Time: 0 minObjectives
learn how to create and access a data frame
learn data frame transformation and operations
Data Frames
Data frames are used for storing Data tables in R. They are two-dimensional array structures and are similar to tables where each column represents one variable. The main features to note about a data frame are:
-
Columns can be of different data types
-
Each column name must be unique
-
Each column should be of the same length i.e., contain the same number of elements
Data frames in R can be created in two ways:
- Using data.frame() command
- Importing data from files such as .csv, .xlsx etc.
data.frame() FUNCTION:
While using the command we can follow the below syntax
data. Frame (column_1, column_2, column_3, …………………….)
Make sure that the names of the columns are unique and are of the same length.
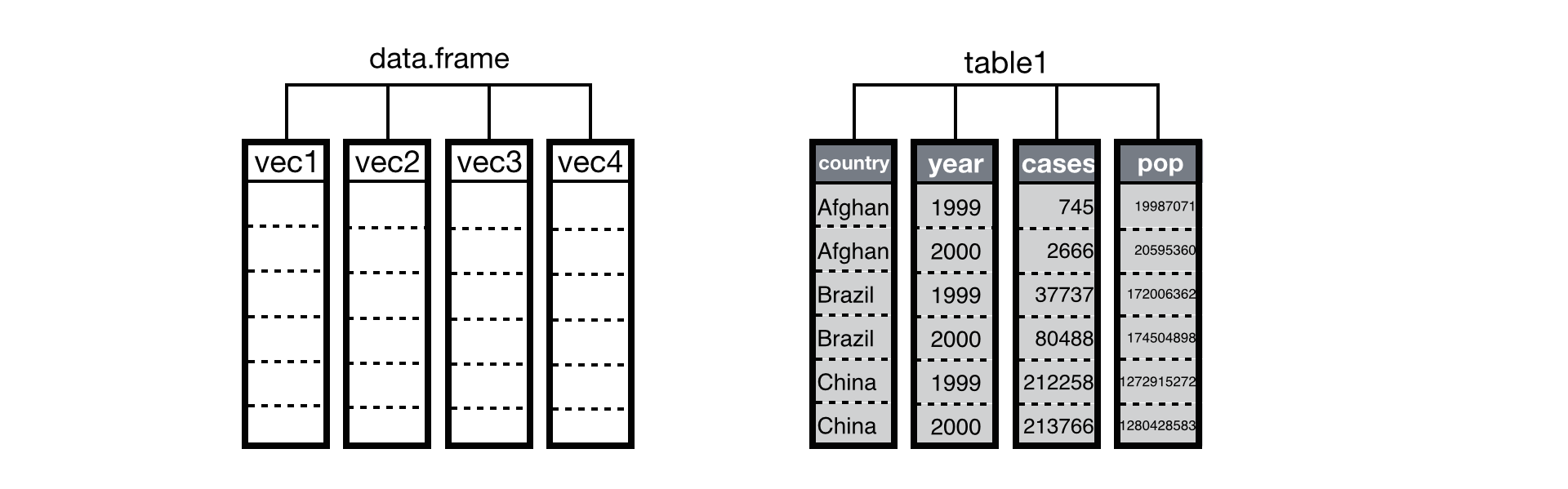
Creating a data frame
# input code
# Student ID, names and their marks.
student.data <- data.frame(
std_id = c(001:005),
std_name = c("William", "James", "Olivia", "Steve", "David"),
std_marks = c(84.8, 98.4, 74.6, 80, 95)
)
# Display the dataframe student.data
student.data
# Check the structure of the dataframe student.data
str(student.data)
#check the head and tail of the dataframe student.data
head(student.data, 3)
tail(student.data, 3)
# Check the summary, lenth and dimension of the dataframe student.data
summary(student.data)
length(student.data)
dim(student.data)
# Check number of row/columns individually.
ncol(student.data)
nrow(student.data)
#output
> # Student ID, names and their marks.
> student.data <- data.frame(
+ std_id = c(001:005),
+ std_name = c("William", "James", "Olivia", "Steve", "David"),
+ std_marks = c(84.8, 98.4, 74.6, 80, 95)
+ )
>
> # Display the dataframe student.data
> student.data
std_id std_name std_marks
1 1 William 84.8
2 2 James 98.4
3 3 Olivia 74.6
4 4 Steve 80.0
5 5 David 95.0
>
> # Check the structure of the dataframe student.data
> str(student.data)
'data.frame': 5 obs. of 3 variables:
$ std_id : int 1 2 3 4 5
$ std_name : chr "William" "James" "Olivia" "Steve" ...
$ std_marks: num 84.8 98.4 74.6 80 95
>
> #check the head and tail of the dataframe student.data
> head(student.data, 3)
std_id std_name std_marks
1 1 William 84.8
2 2 James 98.4
3 3 Olivia 74.6
>
> tail(student.data, 3)
std_id std_name std_marks
3 3 Olivia 74.6
4 4 Steve 80.0
5 5 David 95.0
>
>
> # Check the summary, lenth and dimension of the dataframe student.data
> summary(student.data)
std_id std_name std_marks
Min. :1 Length:5 Min. :74.60
1st Qu.:2 Class :character 1st Qu.:80.00
Median :3 Mode :character Median :84.80
Mean :3 Mean :86.56
3rd Qu.:4 3rd Qu.:95.00
Max. :5 Max. :98.40
>
> length(student.data)
[1] 3
>
> dim(student.data)
[1] 5 3
>
> # Check number of row/columns individually.
> ncol(student.data)
[1] 3
> nrow(student.data)
[1] 5
Accessing Dataframe
# input code
student.dataMaths <- data.frame(
std_id = c(001:005),
std_name = c("William", "James", "Olivia", "Steve", "David"),
std_marks_maths = c(56.7, 60.8, 87.1, 55, 62.7)
)
# select columns
student.dataMaths[1]
student.dataMaths[-2]
#selecting columns ONLY data frames
# give the values as vector
student.dataMaths$std_marks_maths
#dataframe[Rows, Cols]
student.dataMaths[2]
student.dataMaths[2,]
student.dataMaths[c(1:3),]
# output
> student.dataMaths <- data.frame(
+ std_id = c(001:005),
+ std_name = c("William", "James", "Olivia", "Steve", "David"),
+ std_marks_maths = c(56.7, 60.8, 87.1, 55, 62.7)
+ )
>
> # select columns
> student.dataMaths[1]
std_id
1 1
2 2
3 3
4 4
5 5
> student.dataMaths[-2]
std_id std_marks_maths
1 1 56.7
2 2 60.8
3 3 87.1
4 4 55.0
5 5 62.7
>
> #selecting columns ONLY data frames
> # give the values as vector
> student.dataMaths$std_marks_maths
[1] 56.7 60.8 87.1 55.0 62.7
>
> #dataframe[Rows, Cols]
>
> student.dataMaths[2]
std_name
1 William
2 James
3 Olivia
4 Steve
5 David
> student.dataMaths[2,]
std_id std_name std_marks_maths
2 2 James 60.8
>
> student.dataMaths[c(1:3),]
std_id std_name std_marks_maths
1 1 William 56.7
2 2 James 60.8
3 3 Olivia 87.1
Data Transformation
#Input code
student.dataEnglish <- data.frame(
std_id = c(001:005),
std_name = c("William", "James", "Olivia", "Steve", "David"),
std_marks_eng = c(84.8, 98.4, 74.6, 80, 95)
)
student.marks <- data.frame(
student.dataEnglish,
student.dataMaths[3])
student.marks
stud_6 <- data.frame(std_id = c(1:6))
stud_6
stud6_marks <- data.frame(
student.dataEnglish,
stud_6)
student.dataEnglish
new_stdData <- data.frame(
std_id = 006,
std_name = "George",
std_marks_eng = 75.6)
new_stdData
update.stdDataEng <- rbind(student.dataEnglish, new_stdData)
update.stdDataEng
# output
> student.dataEnglish <- data.frame(
+ std_id = c(001:005),
+ std_name = c("William", "James", "Olivia", "Steve", "David"),
+ std_marks_eng = c(84.8, 98.4, 74.6, 80, 95)
+ )
>
> student.marks <- data.frame(
+ student.dataEnglish,
+ student.dataMaths[3])
>
> student.marks
std_id std_name std_marks_eng std_marks_maths
1 1 William 84.8 56.7
2 2 James 98.4 60.8
3 3 Olivia 74.6 87.1
4 4 Steve 80.0 55.0
5 5 David 95.0 62.7
>
> stud_6 <- data.frame(std_id = c(1:6))
> stud_6
std_id
1 1
2 2
3 3
4 4
5 5
6 6
>
> stud6_marks <- data.frame(
+ student.dataEnglish,
+ stud_6)
Error in data.frame(student.dataEnglish, stud_6) :
arguments imply differing number of rows: 5, 6
>
> student.dataEnglish
std_id std_name std_marks_eng
1 1 William 84.8
2 2 James 98.4
3 3 Olivia 74.6
4 4 Steve 80.0
5 5 David 95.0
>
> new_stdData <- data.frame(
+ std_id = 006,
+ std_name = "George",
+ std_marks_eng = 75.6)
>
> new_stdData
std_id std_name std_marks_eng
1 6 George 75.6
>
> update.stdDataEng <- rbind(student.dataEnglish, new_stdData)
>
> update.stdDataEng
std_id std_name std_marks_eng
1 1 William 84.8
2 2 James 98.4
3 3 Olivia 74.6
4 4 Steve 80.0
5 5 David 95.0
6 6 George 75.6
Data Operations
# input code
# Create a dataframe for user data containing their
# IDs, Names, Age and heights in cm.
user.data <- data.frame(
user.sn = c(1:5),
user.name = c("Mr. A", "Mrs B", "Mrs. C", "Mr. D", "Mr. D"),
user.age = c(25, 50, 41, 29, 58),
user.height = c(181, 165, 155, 162, 142)
)
user.data
# Calculating sum of ages
sum(user.data$user.age)
# Calculating the mean of user ages
mean(user.data[[3]])
# Calculating standard deviation of user ages
sd(user.data$user.age)
# Searching for 180 in user.data dataframe
"180" %in% user.data$user.height
"165" %in% user.data$user.height
# output
> # IDs, Names, Age and heights in cm.
> user.data <- data.frame(
+ user.sn = c(1:5),
+ user.name = c("Mr. A", "Mrs B", "Mrs. C", "Mr. D", "Mr. D"),
+ user.age = c(25, 50, 41, 29, 58),
+ user.height = c(181, 165, 155, 162, 142)
+ )
> user.data
user.sn user.name user.age user.height
1 1 Mr. A 25 181
2 2 Mrs B 50 165
3 3 Mrs. C 41 155
4 4 Mr. D 29 162
5 5 Mr. D 58 142
> # Calculating sum of ages
> sum(user.data$user.age)
[1] 203
> # Calculating the mean of user ages
> mean(user.data[[3]])
[1] 40.6
> # Calculating standard deviation of user ages
> sd(user.data$user.age)
[1] 13.86723
>
> # Searching for 180 in user.data dataframe
> "180" %in% user.data$user.height
[1] FALSE
>
> "165" %in% user.data$user.height
[1] TRUE
Key Points
basic statistical knowledge and formulas