Setup
Overview
Time: minObjectives
Install Microsoft Office to use Microsoft Access
Software setup
To practice the database design concepts in this workshop, Microsoft Access, will be used to create a simple database.
Install Microsoft Office
To use Microsoft Access for this workshop, please install Microsoft Office available through UIC Technology Solutions.
Follow the instructions from Technology Solutions to install: Microsoft Office Installation Instructions
Install the videoconferencing client
If you haven't used Zoom before, go to the official website to download and install the Zoom client for your computer.
Set up your workspace
Like other Carpentries workshops, you will be learning by "coding along" with the Instructors. To do this, you will need to have both the window for the tool you will be learning about (a terminal, RStudio, your web browser, etc..) and the window for the Zoom video conference client open. In order to see both at once, we recommend using one of the following set up options:
- Two monitors: If you have two monitors, plan to have the tool you are learning up on one monitor and the video conferencing software on the other.
- Two devices: If you don't have two monitors, do you have another device (tablet, smartphone) with a medium to large sized screen? If so, try using the smaller device as your video conference connection and your larger device (laptop or desktop) to follow along with the tool you will be learning about.
- Divide your screen: If you only have one device and one screen, practice having two windows (the video conference program and one of the tools you will be using at the workshop) open together. How can you best fit both on your screen? Will it work better for you to toggle between them using a keyboard shortcut? Try it out in advance to decide what will work best for you.
Data files:
Please download the following file(s) to participate in the workshop:
Link to Database: Sample_Database
About the Data Used in this Workshop:
The dataset used is a sample dataset for executing queries on MS Access. It is a basic data on tables like Customer, Purchase and Items.
Key Points
Microsoft Access is available in the Microsoft Office Suite
Microsoft Office is available through UIC Technology Solutions
Intro to Database
Overview
Time: 12 minObjectives
To understand the concepts of databases
Introduction to Databases
Data is available in large amounts in the current time and databases help store these data. A database is a collection of data which it holds in a structed format. Data from a database can be accessed in multiple ways.
Database Management Systems (DBMS)
DBMS is a software which is used to store, edit, and extract the data in a database. The features of a DBMS help to manage the data in a robust and efficient manner. A DBMS can accept queries from various interfaces and executes them against the data stored in a database and fetches & produces the results.
STRUCTURED vs UNSTRUCTURED DATA:
Structured data are highly organized. They can be mapped into specific fields such as names, country, zip codes etc. They are generally stored and organized in the format of tables and spreadsheets. Structured data are easy to work with and make up 20% of the data currently. Generally structured data are stored in RDBMS (Relational Database Management Systems) and are managed using SQL (Structured Query Language).
Unstructured data on the other hand do not have any pre-defined structure. This data cannot be processed (or) analyzed using any conventional methods/tools. With the Social media boom unstructured data is now being produced at a rapid pace making up 80% of the current data. Examples of this type of data include images, audio, video etc. Unstructured data are generally stored and handled by NoSQL databases.
Key Points
Introduction to Databases, DBMS.
Comparison between Structured and Unstructured Data
Introduction to ER Model
Overview
Time: 20 minObjectives
To get familiarized with the concepts of Relational DBMS and ER Model
To get deeper understanding of various relationships in ER Model
Relational Database Management Systems (DBMS)
A Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS) is a program used to manage a relational database. In a relational database data is mostly organized into tables and the database helps us identify and access data in relation to another data within the database. A single database may comprise of multiple tables and they might be related to each other.
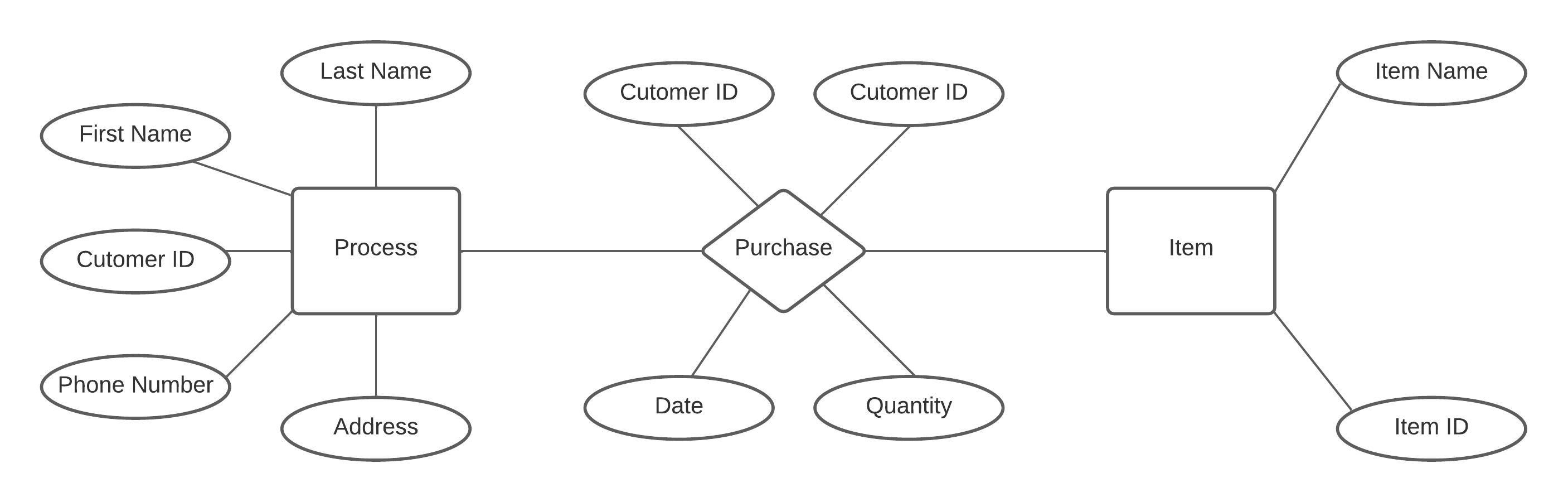
ENTITY–RELATIONSHIP(ER) MODEL
The ER model is used to describe the data in terms of objects (entities) along with the relationships between them. It helps us to understand how the underlying data in an organization are linked to each other.
ENTITY:
-
Entity – An entity is an object of the real world which can be distinguished from other objects. Examples of entities area student in the CS department, a lecturer in the CS department, a teaching assistant in physics department etc.
-
Entity Set – A collection of similar entities is referred to as an Entity set. For example, collection of all employees at a university. An entity may not belong to just one entity set, it can be present in multiple sets, in other words entity sets need not be disjoint. For example a student working as a Teaching Assistant may belong to an entity set, list of all students in a university and another set, all teaching assistant at a university.
-
Attributes – Each entity is described by a set of features called attributes. For a student at UIC, the attributes could be UIN, major, level (Undergrad, Graduate or PhD) etc. All the entities in an entity set are similar and have the same set of attributes.
Each attribute has a particular domain i.e. for Name attribute the domain could be string of length 30, while for UIN would be 9-digit integers. Each entity set also has a primary key, which is an attribute whose value is used to uniquely identify each record (or) entity in the set, e.g. UIN .A list of attributes whose values are unique for each entity is known as candidate key, e.g. UIN, NetID and email.
RELATIONSHIP:
A relationship helps define the relation between different entities i.e. how an entity is related to another. Consider an organization which has two entity sets, Employee and Department. The relationship between them would be “works in” as in employee “works in” a department. Information about the relationship is referred to as descriptive attributes.
Relationship set is a collection of relationships of the same type. For e.g. Employee E1 works in Department D1 is a relationship, while Employees E2, E3, E5, E6 works in Department D2 is a relationship set (since it is a collection of relationships).
A relationship set is represented in a diamond
Types (Cardinality)
Cardinality refers to how many entities in tow entity sets can be related to each other.
- One-to-One: A single entity in an entity set is related to only one single entity in another set
- One-to-Many: A single entity in an entity set is related to multiple entities in another set. The vice versa where multiple entities in one set are related to a single entity in another set is known as many-to-one
- Many-to-Many: Every entity in one set is related to multiple entities in second set and similarly every entity in the second set is related to multiple entities in the first set.
WEAK ENTITY
A weak entity is an entity set which does not have a primary key of its own. They are identified uniquely based on the primary key of another entity. For example, in an organization consider employees purchase policies for their dependents (family members), then the entity set Dependents is a weak entity.
Weak entities are represented using thick rectangular boxes.
Note that Name is not a unique identifier on its own for Dependents entity set. There can be multiple people with the name John under dependents. Once an employee entity is chosen then the Name can be used to uniquely identify the dependents of that particular employee. Hence Name is known as partial key of weak entity set.
Restrictions:
- The relationship of Owner entity set to Weak entity set must be one-to-many (one owner to many weak)
- The weak entity must have complete participation in the identifying relationship
“IS A” HIERARCHY
The IS A hierarchy is used to classify an entity set into subclasses. For e.g. an entity set Employee may be classified into subclasses of Hourly_Employee , Contract_Employee (or) Senior_Employee, Junior_Employee etc. All the attributes of the parent entity set are inherited i.e. present in its subclasses.
Constraints:
-
Overlap – Can one single entity be present in more than one subclass? A single employee cannot be part of both Hourly_Employee & Contract_Employee. But if an entity set has Contract_Employee & Senior_Employee as its subclass then an employee can be present in both subclasses. Can be represented as Contract_Employee OVERLAP Senior_Employee
-
Covering – Does all the entity of subclass cover all the entities of a parent (or) super class. All the entities of Employee parent class may not belong to subclass Hourly_Employee but all entities of Employee parent class may belong to the combined entities set of Hourly_Employee & Contract_Employee. This can be represented as Hourly_Employee AND Contract_Employee COVER Employee.
ER MODEL RULES
Total Participation – All entities of an entity set participate in the relationship. This is represented by a thick line between entity set and relationship in the diagram.
Partial Participation – Not all entities of the entity set will participate in the relationship. This is represented by a thin line between entity set and relationship in the diagram.
At most one – Each entity in this entity set is related to at most one entity in the other entity set it is related. This is indicated by an arrow between entity set and relationship in the diagram.
In the above diagram, there is a total participation by Employee entity with Department entity through works relationship. This indicates that all employees belong to some department in the organization. Similarly, there is a total participation by Department entity with Employee entity through works relationship indicating in each department there is at least one employee working. There is a partial participation by Employee entity with Department entity through the manages relationship. This shows not all employees manage a department but only some. The Department entity has a thick line indicating complete participation with an arrow at the end indicating at most one through the manages relationship. This shows that all departments are manages by some employee (total participation – thick line) but each department is managed by at most one (arrow) employee.
ER diagram of customer purchases a item Database
Key Points
Introduction to ER Model
Explanation of Cardinality, various type of Entity Relationships and the rules of ER Model
Introduction to MS Access
Overview
Time: 45 minObjectives
Introduction to MS Access application
Manipulating data using MS Access
Microsoft Access is a database management tool which is simple to use. It provides an easy, user friendly user interface to create, edit and manage databases.
In a relational database, data is generally stored in the form of tables. Each table here represents an entity set while the columns of the table represent the entity attributes. Each row in the table represents a single entity inside the entity set.
Note: Every UIC student should have free access to Microsoft office product. Once you open MS Access in your device if prompted to sign in, use your UIC email address and password to sign in.
CREATING DATABASE AND TABLES:
- Open MS-Access
- Select Black database option
- Provide a name for the database (e.g. Sample_Database) and then click Create
- Once done the first table is automatically generated
- Now select Create from the menu bar and select Table twice to create two additional tables (entity sets)
- Now rename the 3 tables as: Customer, Item, Purchase. To rename a table, select the table at the top and not on the left pane and then press Ctrl + S
- To create columns (attributes) for a table, select the particular table on top and switch to design view by clicking on View (or) Down Arrow on View → Design View
- In Design View enter the column names (or) attributes for each table as shown in the image below and then save the table before moving to the next table
DATA TYPES – FIELD PROPERTIES & FORMATTING
- MS-ACCESS provided a list of pre-defined data types rom which we need to assign a single data type for each attribute
- Set the Data Type for each attribute by selecting it from the corresponding drop-down box
- The Field Properties box can be located at the bottom of the page when a particular Field or its Data Type is selected in the Design View
- Enter Field Size as 30 for First Name and Last Name and 100 for Address in Customer table
- For Phone Number in Customer table click on Input Mask first and then click on three dots at the end of property
- Now Select Phone Number option and click Next.
- In the next dialog box, replace the 999 with 000 (9 → optional to enter ; 0 → mandatory to enter) and click Next
- In the final dialog box, choose the preferred format to display the number and click Finish
- To set the primary key, select the attribute in Design View and click on the particular attribute and click the primary key icon. To make multiple attributes as primary key, select all the attributes by clicking on the grey box to its left while holding down Ctrl key and click the primary key icon
Set the primary keys as below:
Customer - ID
Item - ID
Purchase - Customer ID, Item ID, Date
- Now Enter a few sample data in all the three tables
RELATIONSHIPS
- Select Database Tools → Relationships to open the relationships window
- Now drag all three tables into the relationship window
- Now click on Customer.ID column and drag & drop it on Purchase.Customer ID column. Check the “Enforce Referential Integrity” checkbox and click Create
Referential Integrity – Helps prevent actions which might affect the relationship. For e.g. Changing only the data type of ID column in Customer table to Text but not the Customer ID column in Purchase table.
- Now repeat the above step with Ite.ID column & Purchase.Item ID column
- Once the relationships have been established the final output looks as below
QUERIES
Queries help fetch data from tables based on the search criteria provided
Query 1 – Items purchased by customers with First Name “Kevin”
- Select Create → Query Design from the menu bar
- Double click on all three tables on the right pane (Add tables) to import them in the query
- In the query Pane below select the columns from the corresponding tables which need to be viewed and set conditions on
- Now in the menu bar select Design and click on RUN
- The final Output will now be displayed as below
Query 2 – Items purchased by customers with First Name “Kevin” OR “Selena”
- Repeat first two steps as Query 1 and now set the below conditions on the corresponding columns (attributes)
- Now RUN the query and you will receive the output as below
Query 3 – Items purchased by customers with First Name “Kevin” AND Quantity greater than 3
- Repeat first two steps as Query 1 and now set the below conditions on the corresponding columns (attributes)
- Now RUN the query and you will receive the output as below
Key Points
design and create databases using MS Access
designing queries to grab required data from databases
Intro Database Exercises
Overview
Time: 20 minObjectives
Practice skills related to introductory database content
ER Diagram exercise
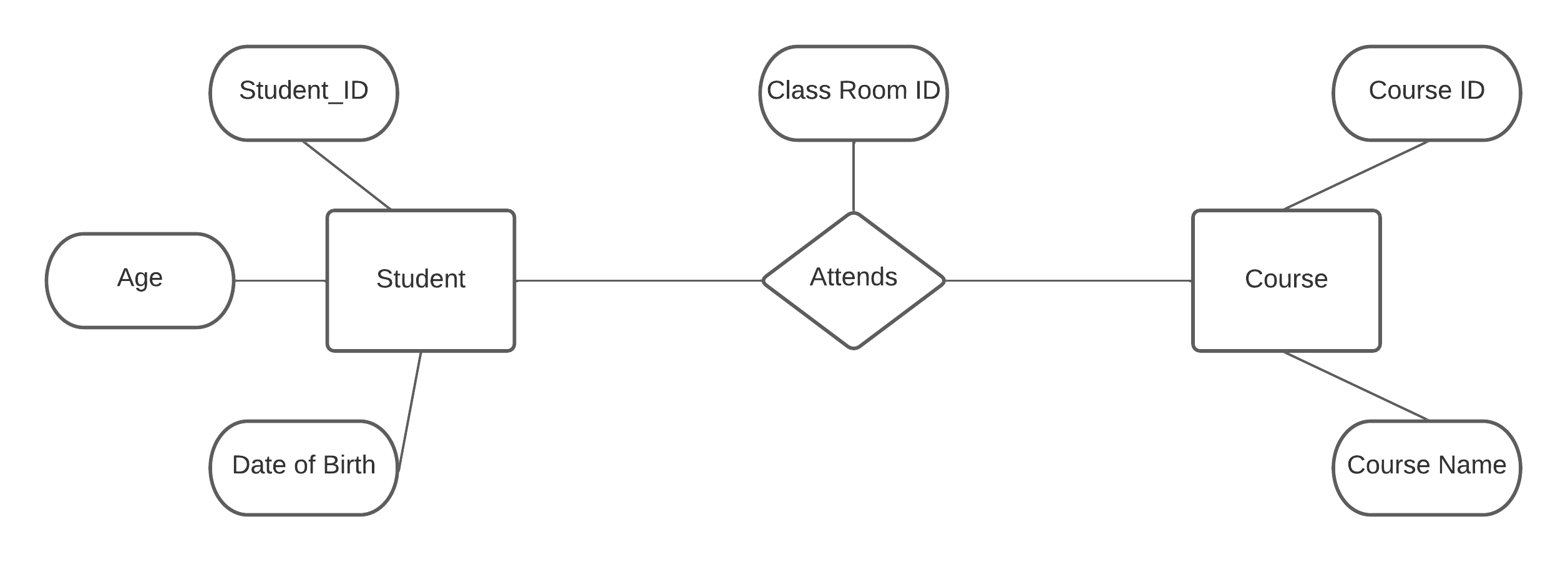
Draw a ER diagram representing the database of students attending courses.
Solution
Multiple solutions possible.
ER diagram of students attending courses
MS Access Database queries exercise 1
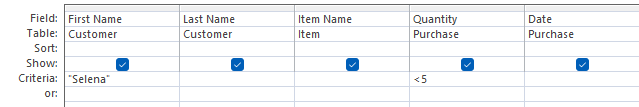
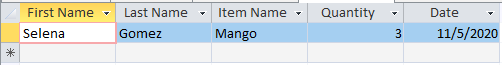
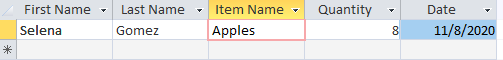
Using MS Access, retrieve the Items purchased by customers with First Name “Selena” AND Quantity less than 5
Solution
Query
Result
MS Access Database queries exercise 2
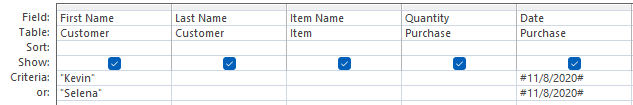
Using MS Access, retrieve the Items purchased by customers with First Name “Kevin” or “Selena” on date 8th November, 2020
Solution
Query
Result
Key Points
Practicing the important topics of the workshop